API stands for Application Programming Interface, and comprises a set of standards that allow two applications to talk to each other. REST APIs are a certain pattern of building APIs. They are based on the HTTP protocol, sending and receiving JSON or XML data through URIs (uniform resource identifier). JSON-based REST APIs are prevalent. We will also be using such one in this tutorial.
OData, which is very popular in the SAP world, is itself a REST API. There is a lot of information out there on how to provide a REST API from ABAP (i.e., to publish an OData service). But there isn’t much on how to consume an external API in ABAP. And from what little there is, it includes non-whitelisted ABAP APIs, i.e., they cannot be used with Cloud ABAP. So, I decided to write this tutorial on consuming REST APIs using Cloud ABAP.
Scenario
API Provider
We will be working with JSON Placeholder – a “free to use fake Online REST API for testing and prototyping”. It will allow us to perform all CRUD (create, read, update, delete) actions. To be fair, the create, update, and delete will not actually work, but the server will fake it as if they do. Which is completely enough for our use-case!
Resources
Our API provider exposes posts, comments, albums, photos, TODOs, and users. For simplicity’s sake, we will only be using the posts resource, and pretend the rest aren’t there. The main idea of my tutorial is to provide an extremely simple guide on how to execute the CRUD actions on a REST API. And do this using whitelisted ABAP APIs in the SAP Cloud Platform (CP). This means that you can run this code on a SAP CP trial account.
Posts resource
A post has an ID, title, body and user ID, meaning the ID of the user that created the post. We represent it in ABAP as follows:
TYPES:
BEGIN OF post_s,
user_id TYPE i,
id TYPE i,
title TYPE string,
body TYPE string,
END OF post_s,
post_tt TYPE TABLE OF post_s WITH EMPTY KEY,
BEGIN OF post_without_id_s,
user_id TYPE i,
title TYPE string,
body TYPE string,
END OF post_without_id_s.
We need the structure without ID because the post ID is automatically assigned by the REST API. Meaning that we do not provide it when creating a new post.
Cloud ABAP APIs used
Sending HTTP requests
As I mentioned earlier, the small number of existing tutorials for consuming REST APIs in ABAP primarily use non-whitelisted ABAP APIs. For example, the if_http_client one, whose use is not permitted in Cloud ABAP. The way to check the whitelisted ABAP APIs for the SAP Cloud Platform is to browse the Released Objects lists. It is accessible in Eclipse ABAP Development Tools (ADT) -> Project Explorer -> Released Objects. So, the cloud-ready ABAP API to send HTTP request is the if_web_http_client. We define the following method to get a client:
[definition]
METHODS:
create_client
IMPORTING url TYPE string
RETURNING VALUE(result) TYPE REF TO if_web_http_client
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD create_client.
DATA(dest) = cl_http_destination_provider=>create_by_url( url ).
result = cl_web_http_client_manager=>create_by_http_destination( dest ).
ENDMETHOD.
Notice that the URL is an input parameter. The returned result is the created web HTTP client.
Working with JSON
To work with JSON, we will be using the Cloud Platform edition of the XCO (Extension Components) library. The specific class, relevant to our use case is xco_cp_json. Something extremely valuable it provides is the ability to transform different naming conventions. For example, camelCase to under_score, and the other way around.
Consuming the REST API
Before getting to the fun part, we just have to define a few constants. Of course, this is not strictly necessary, but working with constants as opposed to string literals is a better practice, and allows for reusability.
CONSTANTS:
base_url TYPE string VALUE 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts',
content_type TYPE string VALUE 'Content-type',
json_content TYPE string VALUE 'application/json; charset=UTF-8'.
The base URL is simply the address of the posts resource. The latter two constants we need for the cases where we will be sending data (i.e., create and update) to the server using the REST API. We have to let the server know we are sending JSON.
Read all posts
The URL for reading all posts is just the base URL. So, we create a client for it, use the client to execute a GET request, close the client, and convert the received JSON to a table of posts. The table of posts type is defined in the Posts resource section above. You can also refer to the full code at the end.
[definition]
read_posts
RETURNING VALUE(result) TYPE post_tt
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD read_posts.
" Get JSON of all posts
DATA(url) = |{ base_url }|.
DATA(client) = create_client( url ).
DATA(response) = client->execute( if_web_http_client=>get )->get_text( ).
client->close( ).
" Convert JSON to post table
xco_cp_json=>data->from_string( response )->apply(
VALUE #( ( xco_cp_json=>transformation->camel_case_to_underscore ) )
)->write_to( REF #( result ) ).
ENDMETHOD.
Read single post
The method to read a single post is similar, with the differences that we take as an input an ID of the post, and return a structure (i.e., a single post,) instead of a table (i.e., a list of posts). The REST API’s URL of reading a single post is as follows:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/{ID}
[definition]
read_single_post
IMPORTING id TYPE i
RETURNING VALUE(result) TYPE post_s
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD read_single_post.
" Get JSON for input post ID
DATA(url) = |{ base_url }/{ id }|.
DATA(client) = create_client( url ).
DATA(response) = client->execute( if_web_http_client=>get )->get_text( ).
client->close( ).
" Convert JSON to post structure
xco_cp_json=>data->from_string( response )->apply(
VALUE #( ( xco_cp_json=>transformation->camel_case_to_underscore ) )
)->write_to( REF #( result ) ).
ENDMETHOD.
Create post
As explained earlier, posts’ IDs are automatically assigned by the REST API. So, to create a post we will be using the post_without_id_s type. This will be our input parameter. We are going to convert from this ABAP structure to JSON, once again using the XCO library. From there, we create a client. Then, we set the body of the HTTP request we are going to send to be the JSON we just created and we let the server know that we will be sending JSON content-type. Lastly, we execute a POST request, and return the server’s response. If all went good, the server’s response would return us our post, along with its newly generated ID (101, because there are currently 100 posts).
[definition]
create_post
IMPORTING post_without_id TYPE post_without_id_s
RETURNING VALUE(result) TYPE string
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD create_post.
" Convert input post to JSON
DATA(json_post) = xco_cp_json=>data->from_abap( post_without_id )->apply(
VALUE #( ( xco_cp_json=>transformation->underscore_to_camel_case ) ) )->to_string( ).
" Send JSON of post to server and return the response
DATA(url) = |{ base_url }|.
DATA(client) = create_client( url ).
DATA(req) = client->get_http_request( ).
req->set_text( json_post ).
req->set_header_field( i_name = content_type i_value = json_content ).
result = client->execute( if_web_http_client=>post )->get_text( ).
client->close( ).
ENDMETHOD.
Update post
We will be updating with a PUT request. This means we will provide the full post. PATCH, on the other hand, allows us to only provide the updated field (e.g., only title). If you find this interesting, you could try to make the PATCH request yourself – it shouldn’t be too hard with the provided here resources!
We follow a similar logic as with the create action. We also provide a post as an input parameter, but this time we use the full structure (with post ID). The URL for updating a post is the same as accessing this (single) post:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/{ID}
So, the only differences from create include the changed type of the post input parameter, the URL, and the HTTP request method (PUT).
[definition]
update_post
IMPORTING post TYPE post_s
RETURNING VALUE(result) TYPE string
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD update_post.
" Convert input post to JSON
DATA(json_post) = xco_cp_json=>data->from_abap( post )->apply(
VALUE #( ( xco_cp_json=>transformation->underscore_to_camel_case ) ) )->to_string( ).
" Send JSON of post to server and return the response
DATA(url) = |{ base_url }/{ post-id }|.
DATA(client) = create_client( url ).
DATA(req) = client->get_http_request( ).
req->set_text( json_post ).
req->set_header_field( i_name = content_type i_value = json_content ).
result = client->execute( if_web_http_client=>put )->get_text( ).
client->close( ).
ENDMETHOD.
Delete post
Deleting a post is the simplest request. We simply take the ID, and send a DELETE HTTP request to the URL of the specific post. To let the user if something goes wrong, we check the server’s response code (should be 200 – meaning OK).
[definition]
delete_post
IMPORTING id TYPE i
RAISING cx_static_check
[implementation]
METHOD delete_post.
DATA(url) = |{ base_url }/{ id }|.
DATA(client) = create_client( url ).
DATA(response) = client->execute( if_web_http_client=>delete ).
IF response->get_status( )-code NE 200.
RAISE EXCEPTION TYPE cx_web_http_client_error.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.
Testing our code
Now that we have provided all the CRUD functionalities, let’s check them out! To do this, we will be implementing the if_oo_adt_classrun interface, which allows to run a class as a console application. It has a main method that gets executed – similar to Java.
METHOD if_oo_adt_classrun~main.
TRY.
" Read
DATA(all_posts) = read_posts( ).
DATA(first_post) = read_single_post( 1 ).
" Create
DATA(create_response) = create_post( VALUE #( user_id = 7
title = 'Hello, World!' body = ':)' ) ).
" Update
first_post-user_id = 777.
DATA(update_response) = update_post( first_post ).
" Delete
delete_post( 9 ).
" Print results
out->write( all_posts ).
out->write( first_post ).
out->write( create_response ).
out->write( update_response ).
CATCH cx_root INTO DATA(exc).
out->write( exc->get_text( ) ).
ENDTRY.
ENDMETHOD.
Running with F9 prints the following output:

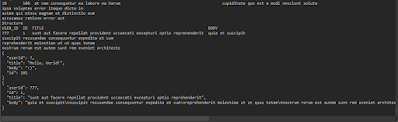
No comments:
Post a Comment