Introduction
This Blog post Gives the basic over view of the numeric Functions , syntax ,data types accepted for that numeric functions , screenshots of output and observations .
Paragraph Body
I have took the simple example of SPFLI table Paymentsum Field To Numeric Functions.
In This example for Highlighted Row value of paymentsum field is 168541.80 .
CEIL Function:
once after performing ceil operation its changed from 168541.80 to next highest integral value 168542
so we can say CEIL operation will give the next integer value of current value if its having decimal part.
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
CEIL(arg)
|
INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8, DEC, CURR, QUAN, FLTP |
INT4, INT8 (if arg is of type INT8) |
If the current value of field is not having any decimal part .
The value stays as it is as shown above in Highlighted Records.
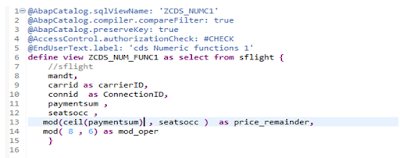
Floor Function:
Floor Operation Removes The Decimal Part and gives only Integer part of the value .
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
FLOOR(arg)
|
INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8, DEC, CURR, QUAN |
Data type of arg for the integer types, else DEC without decimal places |
It Eliminates all the decimal part of the number and shows only integer part.
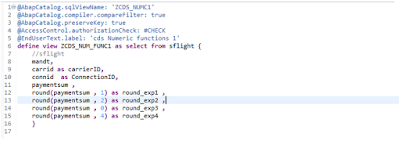
Round Function:
Rounded value of arg If pos is greater than 0, the value is rounded to the position pos on the right of the decimal separator. If this is not the case, position abs(pos)+1 to the left of the decimal separator is rounded. This results in a 0 if the number of places is not sufficient.
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
ROUND(arg, pos)
|
arg: INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8, DEC, CURR, QUAN
pos: Literal, field of a data source or input parameter of type INT1, INT2, INT4
|
Data type of arg, where INT1 and INT2 are transformed to INT4 |
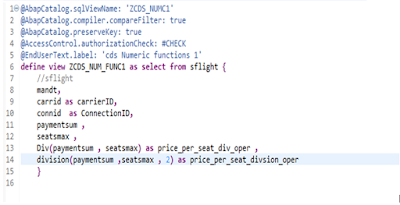
Code:
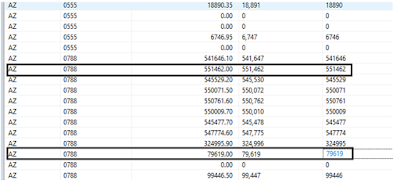
In The above Example I am applying round operation on the same argument Paymentsum With diffenent round positions.
Result:
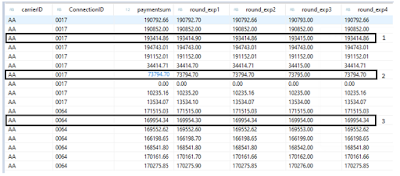
Explanation:
In the above pic we can see that the original field value is having decimal points after integer.
In the 1st Highligted record when the round operation is applied to the value 193414.86 with position value 1(round_exp1) the function finds the nearest rounded value which is 193414.90 , the same value with position value 2 or >2 (Round_exp2) it displays value as it is , now here i can see two digit after decimal place . for ex: if the value is 193414.8626345 can see only 2 numerical digits after decimal rounding as 193414.8600000. Similarly for the same value with position 0(round_exp3) i can see only integer values with decimal part rounded to 0’s as shown 193414.00 .
In the 2nd Highlighted Record The original value has already rounded 73794.70 it will not have any effect if we perform round operation on it because the purpose is already fulfilled.
In the 3rd Highlighted Record The original value is 169954.34 with position value 1(round_exp1) the function finds the nearest rounded value which is 169954.30 .
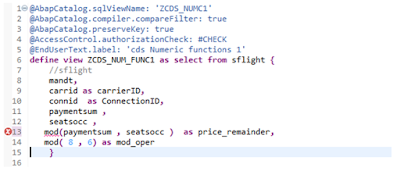
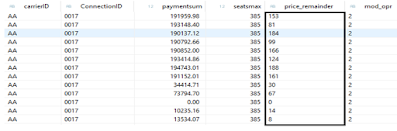
MOD Function:
Mod operation will give the Positive or negative integer remainder of the division of arg1 by arg2.
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
MOD(arg1, arg2)
|
INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8 |
Data type of arg1
|
MOD operation accepts only Integer values as type of the Argument.
Code :
Explanation:
In the above example i am calculating the alias filed price_remainder by applying mod operation on paymentsum and seatocc since paymetsum field is of type currency its howing error because MOD Function will accept only Integer type as argument hence i have applied CEIL function on paymentsum which gives integer type of paymentsum during runtime Shown below to get MOD.
Result:
Usually in real time scenarios CAST operation must be used to convert the data type of the argument on which MOD operation is to be applied in Composite view if data type of argument is not Integer .
Remainder of Paymentsum / seatocc = price_remainder as shown below.
Div and Division Function:
Div operator: Integer part of the division of arg1 by arg2 The sign is assigned after the amounts are divided; positive if the arguments have the same sign, and negative if the arguments have different signs. Exception: arg2 has the value 0.
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
DIV(arg1, arg2)
|
INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8, DEC, CURR, QUAN without decimal places. |
Data type arg1, where DEC, CURR and QUAN are implemented after INT4
|
Division Operater : Division of arg1 by arg2 The result is rounded to dec decimal places.
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
DIVISION(arg1, arg2, dec
|
Division of arg1 by arg2 The result is rounded to dec decimal places. |
DEC with dec decimal places. The length of the result is the length of arg1 minus the decimal places in arg1 plus the decimal places in arg2 plus dec. This value must not be greater than 31.
|
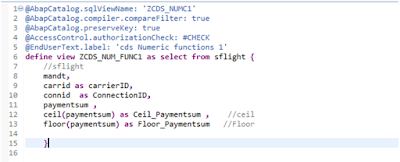
Code
Explanation:
Div and Division operater both will perform division of arg1 / arg2 (paymentsum / seatmax in this case )
And give the quotient as result but only Difference is Div operator will not display decimal part where
as Division Operator will Display The Decimal Rounded Digits as per the value in arg3 place.
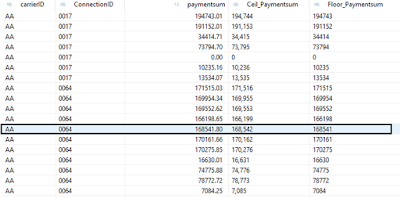
Result :
Division function gives quotient where as MOD gives Remainder.
Difference Between MoD and Div Functions with signs.
The SQL functions DIV and MOD behave differently with respect to the signs than the ABAP operators DIV and MOD. In the SQL function DIV, the amounts of the arguments are divided and then the sign is assigned (positive if the arguments have the same signs and negative if they have different signs). Accordingly, the result of MOD can be negative, so that multiplying the result of DIV by expr2 plus the result of MOD produces the value of expr1. The ABAP operator MOD, on the other hand, only produces positive results.
Division function gives quotient where as MOD gives Remainder.
Example
The following table shows the results of integer divisions and their integer remainders in SQL.
| EXP1 |
EXP2 |
DIV |
MOD |
| 7 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
| -7 |
3 |
-2 |
-1 |
| 7 |
-3 |
-2 |
1 |
| -7 |
-3 |
2 |
-1 |
ABS Operater : Will give only positive valued output .
Syntax:
| Function |
Valid Argument Types |
Result Type |
|
ABS( arg )
|
INT1, INT2, INT4, INT8, DEC, CURR, QUAN, FLTP
|
Data type of arg.
Absolute amount of arg.
|
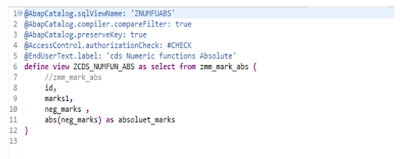
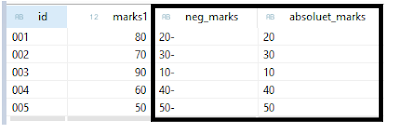
Explanation:
In this cds view i am displaying 3 columns having student id(id) , marks(marks1) and negative marks(neg_marks), the field neg_marks having –ve marks, I converted it to +ve values using the numeric function ABS On neg_marks [abs(neg_marks) as absolute_marks].
Result:



No comments:
Post a Comment