Parent child relationship in CDS data modeling for ABAP RESTful application programming model (RAP)
The ABAP RESTful application programming model (RAP) defines the architecture for efficient end-to-end development of intrinsically SAP HANA-optimized OData services (such as Fiori apps) in SAP Cloud Platform, ABAP Environment or Application Server ABAP.
Target group
◉ You are an ABAP developer and use CDS views for data modeling
◉ You are a newbie to ABAP RESTful programming model (RAP)
◉ You like to get few insights into RAP and build composition tree(parent-child) into CDS views
So, lets define a simple business use case and build composition tree with CDS
Prerequisites:
◉ ABAP Platform for S/4Hana 1909 or SAP Cloud Platform, ABAP environment
◉ ABAP Development Tools (ADT)
Scenario:
◉ Develop a business application for a travel agency with ABAP RESTful programming model
◉ The travel agency can book travel trips for customers
◉ The travel trip can include multiple bookings
◉ Each booking can include multiple booking supplements like refreshments during flight
◉ The relevant travel, booking and booking supplement data will be provided via UI (web IDE/BAS)
Requirements:
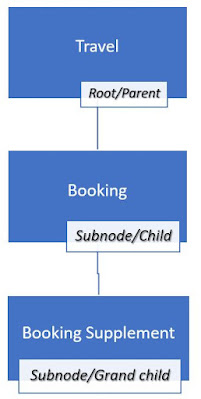
◉ The business object should represent a parent child hierarchy
◉ Travel is the root entity for the hierarchy.
◉ Booking is the child node of travel
◉ Booking supplement is grandchild node of travel
◉ A travel can exist without a valid booking – only root as single node is allowed
◉ A booking cannot exist without a valid travel – no orphans allowed
◉ A booking supplement cannot exist without a booking-– no orphans allowed
◉ Possibility to create, update and delete any node-no orphans allowed
◉ Perform calculations, validate input values and reject instance creation (if needed)
Travel Agency BO
Data modeling:
◉ Create database tables for data persistence and create parent-child relationship via foreign key associations
◉ In this scenario, primary keys-travel_id, booking_id and booking_supplement_id are sematic keys
◉ DB table for Travel entity has travel_id as primary key
◉ Any new travel(instance) created for travel entity will be identified with this primary key
◉ DB table for Booking entity has booking_id and travel_id as primary keys
◉ Any new booking(instance) created for entity booking should belong to entity set travel
◉ This means, travel is the parent entity and bookings are child entities
◉ Field travel_id of DB table for Booking entity has a foreign key relationship to field travel_id of DB table for travel entity
◉ Any new booking supplement(instance) created for entity booking supplement should belong to entity set travel
◉ Entity booking supplement has booking entity as parent and travel entity as root
◉ DB table for Booking supplement entity has a foreign key relationship to field booking_id and travel_id of DB table for booking entity
Please note:
◉ Foreign key relation is not mandatory to build a composition tree
◉ It is recommended to have foreign key association
Persistence tables
Note:
◉ For interface views, new version of CDS views-CDS view entities (DEFINE VIEW ENTITY…) are used (these currently only supported in SAP Cloud Platform, ABAP environment)
◉ You can also use existing CDS DDIC-managed views with DEFINE VIEW …. (you must use these in SAP S/4 HANA on premise systems, but it is planned to support view entities in future releases here as well)
◉ Create interface CDS view entities for corresponding database tables and build parent-child relationship via compositions to parent and child
◉ These interface views not service agnostic and reusable in multiple business applications
◉ Interface view for Travel is indicated with DEFINE ROOT VIEW ENTITY ZHB_I_TRAVEL_TCVE as Travel
◉ Usage of ROOT syntax makes Travel as entity set and parent node
◉ Interface view for Booking is indicated with DEFINE VIEW ENTITY ZHB_I_BOOKING_TCVE as Booking
◉ Usage of composition of ZHB_I_BOOKING_TCVE as _Booking syntax makes Travel as parent and booking as child
◉ Interface view for Booking supplement is indicated with DEFINE VIEW ENTITY ZHB_I_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE
◉ Usage of composition of ZHB_I_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE as _BookingSupplement syntax makes booking as parent and booking supplement as child
Best practices:
◉ When defining a parent child relationship, you have to perform changes in both the parent and the child entity.
◉ Since these changes depend on each other you have to use mass activation when you edit both sources at the same time.
◉ When you want to perform the changes in a sequential way you have to start with defining the association to parent in the child entity.
◉ After having activated your changes in the child entity you can then define the composition in the parent entity that points to the child entity.
◉ Example: It is preferred to define association to parent ZHB_I_TRAVEL_TCVE in entity booking and then composition of ZHB_I_BOOKING_TCVE in entity travel
CDS view entities
◉ Create projection CDS view entities for corresponding interface views
◉ Via REDIRECTED TO syntax project the parent-child relationships defined in interface views
◉ These projection views are service agnostic and dedicated to a single business application
◉ Projection view for Travel as parent is indicated with DEFINE ROOT PROJECTION VIEW ENTITY ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE
◉ Usage of redirected to composition child ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE syntax defines ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE (Travel) as parent and ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE (Booking) as child
◉ Projection view for Booking is indicated with DEFINE PROJECTION VIEW ENTITY ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE
◉ Usage of redirected to parent ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE syntax defines ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE(Travel) as parent and ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE (Booking) as child
◉ Usage of redirection to composition child composition of ZHB_C_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE syntax defines ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE (Booking) as parent and ZHB_C_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE (Booking supplement) as child
◉ Projection view for Booking supplement is indicated with DEFINE PROJECTION VIEW ENTITY /DMO/C_BUKSU_CVE
◉ Usage of redirected to parent ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE syntax defines ZHB_C_BOOKING_TCVE(BOOKING) as parent and ZHB_C_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE (Booking supplement) as child
◉ In some cases, it is necessary for the grandchild (Booking supplement) or any node at the end of parent-child relation (for example nth node) to have a direct association with root node
◉ For this scenario, Usage of redirected to ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE (root) syntax in projection entity ZHB_C_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE is used, when
◉ Interface view ZHB_I_BOOKING_SUPPLEMENT_TCVE (grandchild) has an association to ZHB_I_TRAVEL_TCVE (root) – association to ZHB_I_TRAVEL_TCVE as _Travel on $projection.travel_id = _Travel.Travel_ID
◉ In this case, usage of redirected to ZHB_C_TRAVEL_TCVE syntax in projection view defines association b/w nth node and root node
Projection view entities
Next steps to continue with development of oData service:
◉ Create a service definition to define the service model that is generically derived from the previously created CDS-based data model
◉ Create a service binding to bind a service definition to a client-server communication protocol such as OData
Source: sap.com




No comments:
Post a Comment