Recently during my self study on PostgreSQL I made some practice to connect PostgreSQL in Java programming using Java Database Connectivity – JDBC. In fact I found out that there are lots of commonality between these two technologies.
There is a demo program demo_adbc_query mentioned in SAP help to demonstrate the use of ADBC.
I make some changes on it in order to perform a line-by-line comparison with JDBC.
The source code of adapted program:
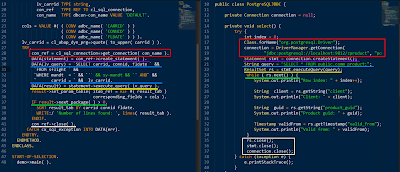
REPORT zjerry_adbc.
CLASS demo DEFINITION.
PUBLIC SECTION.
CLASS-METHODS main.
PRIVATE SECTION.
CLASS-DATA: BEGIN OF result_line,
carrid TYPE sflight-carrid,
connid TYPE sflight-connid,
fldate TYPE sflight-fldate,
END OF result_line,
result_tab LIKE TABLE OF result_line.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS demo IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD main.
DATA: carrid TYPE sflight-carrid VALUE 'AA',
cols TYPE adbc_column_tab,
lv_carrid TYPE string,
con_ref TYPE REF TO cl_sql_connection,
con_name TYPE dbcon-con_name VALUE 'DEFAULT'.
cols = VALUE #( ( CONV adbc_name( 'CARRID' ) )
( CONV adbc_name( 'CONNID' ) )
( CONV adbc_name( 'FLDATE' ) ) ).
lv_carrid = cl_abap_dyn_prg=>quote( to_upper( carrid ) ).
TRY.
con_ref = cl_sql_connection=>get_connection( con_name ).
DATA(statement) = con_ref->create_statement( ).
DATA(lv_query) = `SELECT carrid, connid, fldate ` &&
`FROM sflight ` &&
`WHERE mandt = ` && `'` && sy-mandt && `' AND` &&
` carrid = ` && lv_carrid.
DATA(result) = statement->execute_query( lv_query ).
result->set_param_table( itab_ref = REF #( result_tab )
corresponding_fields = cols ).
IF result->next_package( ) > 0.
SORT result_tab BY carrid connid fldate.
WRITE:/ 'Number of lines found: ', lines( result_tab ).
ENDIF.
con_ref->close( ).
CATCH cx_sql_exception INTO DATA(err).
ENDTRY.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
START-OF-SELECTION.
demo=>main( ).
And now have a look at how JDBC can achieve the same.
I have replicated an ABAP table COMM_PRODUCT to my local PostgreSQL server:
There is a demo program demo_adbc_query mentioned in SAP help to demonstrate the use of ADBC.
I make some changes on it in order to perform a line-by-line comparison with JDBC.
The source code of adapted program:
REPORT zjerry_adbc.
CLASS demo DEFINITION.
PUBLIC SECTION.
CLASS-METHODS main.
PRIVATE SECTION.
CLASS-DATA: BEGIN OF result_line,
carrid TYPE sflight-carrid,
connid TYPE sflight-connid,
fldate TYPE sflight-fldate,
END OF result_line,
result_tab LIKE TABLE OF result_line.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS demo IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD main.
DATA: carrid TYPE sflight-carrid VALUE 'AA',
cols TYPE adbc_column_tab,
lv_carrid TYPE string,
con_ref TYPE REF TO cl_sql_connection,
con_name TYPE dbcon-con_name VALUE 'DEFAULT'.
cols = VALUE #( ( CONV adbc_name( 'CARRID' ) )
( CONV adbc_name( 'CONNID' ) )
( CONV adbc_name( 'FLDATE' ) ) ).
lv_carrid = cl_abap_dyn_prg=>quote( to_upper( carrid ) ).
TRY.
con_ref = cl_sql_connection=>get_connection( con_name ).
DATA(statement) = con_ref->create_statement( ).
DATA(lv_query) = `SELECT carrid, connid, fldate ` &&
`FROM sflight ` &&
`WHERE mandt = ` && `'` && sy-mandt && `' AND` &&
` carrid = ` && lv_carrid.
DATA(result) = statement->execute_query( lv_query ).
result->set_param_table( itab_ref = REF #( result_tab )
corresponding_fields = cols ).
IF result->next_package( ) > 0.
SORT result_tab BY carrid connid fldate.
WRITE:/ 'Number of lines found: ', lines( result_tab ).
ENDIF.
con_ref->close( ).
CATCH cx_sql_exception INTO DATA(err).
ENDTRY.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
START-OF-SELECTION.
demo=>main( ).
And now have a look at how JDBC can achieve the same.
I have replicated an ABAP table COMM_PRODUCT to my local PostgreSQL server:
And I manually inserted two test records into it:
Both is the source code implemented in Java to perform a query against this table and display result:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
public class PostgreSQLJDBC {
private Connection connection = null;
private void select() {
try {
int index = 0;
Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:postgresql://localhost:9812/zproduct", "postgres", "XXXXXX");
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
String query = "SELECT * FROM public.comm_product;";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
while ( rs.next() ) {
System.out.println("Row index: " + index++);
String client = rs.getString("client");
System.out.println("Client: " + client);
String guid = rs.getString("product_guid");
System.out.println("Product guid: " + guid);
Timestamp validFrom = rs.getTimestamp("valid_from");
System.out.println("Valid from: " + validFrom);
}
rs.close();
stmt.close();
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
PostgreSQLJDBC jdbcTest = new PostgreSQLJDBC();
jdbcTest.select();
}
}
Output in console:
And I mark the corresponding part in both language which has the same semantic meaning with same color ( although grammar is different ).
Through this comparison we can know that both connectivity technology follow the same idea.


No comments:
Post a Comment