During my recent CDS view explore I have experienced several ways of CDS view annotation declaration or generation. I list them in this blog for study purpose.
Approach 1: developer does not declaration explicitly, but backend generates automatically
Take this field for example:
Approach 1: developer does not declaration explicitly, but backend generates automatically
Take this field for example:
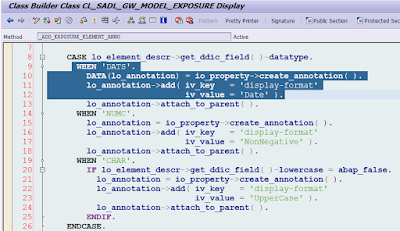
I do not declare any display format on this field. It has DATS data type in the backend.
When you publish this CDS view as OData service and check its metadata response, you can find the annotation “sap:display-format=Date” is automatically added. Who adds it?
Answer: it is added here. Backend framework will automatically add corresponding annotation according to the data type of exposed field.
Approach 2: developer adds one style of annotation, and backend framework detects such annotation, and do some conversion
One example of this kind of approach can already be found from tutorial 7 – unveil the secret of @ObjectModel.readOnly
In that tutorial I explained how the annotation defined by developer ( @ObjectModel.readOnly: true ) is converted by backend framework into sap:updatable = false.
@ObjectModel.readOnly: true
Z_i_Order_View.posting_date
We can also look into another example. We have use the following annotation “@Consumption.valueHelp: ‘_statusfixedvalue’ ” to assign a value help to field txt04:
@Consumption.valueHelp: ‘_statusfixedvalue’
Z_i_Order_View.txt04,
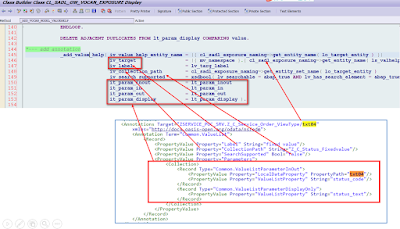
When framework has scanned the annotation in line 47, it will set flag lv_consumption_vh as true.
Base on the fact whether the assigned value help is a consumption or foreign key value help, different element name are put to internal table lt_param_display and finally all the left annotation necessary for value help is generated by framework:
And this picture below explains where does each field in metadata response come from. The logic in method _add_value_help is very useful as it teaches us how to create necessary annotation via ABAP code, which we will use later.
Approach 3: developer adds necessary annotation via ABAP code
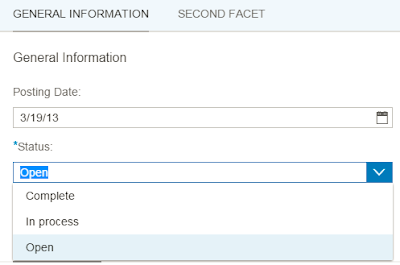
If you would like to build a drop down list based on a CDS view field like the status field below,
it is not just enough to use the annotation “Consumption.valueHelp” in CDS view source code – you would just get a drop down list with technical code of status value displayed. Instead, you must tell Smart template framework to display status description text in drop down list.
In order to archieve it, you must add the following ABAP code in DEFINE method of the MPC_EXT class of your OData service, to tell the framework that the text property for “status_code” is “status_text” by annotation. The usage of such coding to create annotation by ABAP code is learned from method _add_value_help mentioned in approach 2.
lo_txt_property = model->get_entity_type( 'Z_C_Status_FixedvalueType' )->get_property( 'status_code' ).
lo_txt_property->set_value_list( /iwbep/if_mgw_odata_property=>gcs_value_list_type_property-fixed_values ).
lo_text_anno = lo_txt_property->/iwbep/if_mgw_odata_annotatabl~create_annotation( 'sap' ).
lo_text_anno->add( iv_key = 'text' iv_value = 'status_text').
Approach 4: developer adds UI related annotation in CDS view which are consumed by UI5 SmartTemplate
All UI related annotation which could be inserted into CDS view source code could be found from SAP help.
Those UI annotations will not be converted by ABAP backend:
@UI.identification: [ { position: 10 } ]
Z_i_Order_View.posting_date
All UI related annotations could be retrieved via the url below:
And in the runtime, Smart-template also uses this very url to retrieve UI annotations so that it can know what styles of UI control the annotated CDS view field must be rendered as.







No comments:
Post a Comment