Weighbridges are connected to the radiation detector panels through which a vehicle passes and then reaches the weighbridge. The corresponding radiation vales are saved in the radiation detection system.
The purpose of this blog is to explain how this integration picks the radiation values automatically in SAP Screen of Scrap Receiving System (SRS – A custom built application in SAP) and to eliminate the need of manual entry, thereby saving time and eliminating manual entry error.
The purpose of this blog is to explain how this integration picks the radiation values automatically in SAP Screen of Scrap Receiving System (SRS – A custom built application in SAP) and to eliminate the need of manual entry, thereby saving time and eliminating manual entry error.
Data from radiation detector system is available on TCP/IP Port only (Unlike the Weigh Bridge System where data is available on Serial Port).
The radiation detector system has a fixed IP address say 10.1.2.3 and when this IP is queried through command prompt using TELNET, Port 9000, Command RC0101 then it gives the output as shown below.
Now our purpose is to write this output to a file and then read this file when SAP transaction is run.
This is achieved by writing a PowerShell script that does all the activity of TELNET and writes the output to the user PC. This file is then read in SAP Transaction.
Following are the steps to achieve this:
Steps:.
1. Write a PowerShell script
File Name: Get-Radiation.ps1
#Call of this script should be as follows:
#Get-Radiation -RemoteHost "10.1.2.3" -OutputPath "\\WB-SYSTEM\RADCOMM\output.txt"
Param (
[Parameter(ValueFromPipeline=$true)]
[string]$RemoteHost = "10.1.2.3",
[string]$Port = "9000",
[int]$WaitTime = 1000,
[string]$OutputPath = "\\user-pc\RADCOMM\output.txt"
)
$Socket = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient($RemoteHost, $Port)
If ($Socket)
{ $Stream = $Socket.GetStream()
$Writer = New-Object System.IO.StreamWriter($Stream)
$Buffer = New-Object System.Byte[] 1024
$Encoding = New-Object System.Text.AsciiEncoding
$Writer.WriteLine("RC0101")
$Writer.Flush()
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (1000)
$Result = ""
#Save all the results
While($Stream.DataAvailable)
{ $Read = $Stream.Read($Buffer, 0, 1024)
$Result += ($Encoding.GetString($Buffer, 0, $Read))
}
}
Else
{ $Result = "Unable to connect to host: $($RemoteHost):$Port"
}
#Done, now save the results to a file
$Result | Out-File $OutputPath
2. Maintain the above PowerShell script file on SAP Server at folder mentioned in SM49
(For example, R:\RADCOMM\Get-Radiation.ps1)
3. Maintain command ZGET_RADIATION in SM49
Check mark “Additional Parameters Allowed” since two additional parameters will be sent through code
1. RemoteHost (Radiation system IP Address) and
2. OutputPath (Writing the telnet output on WB PC from where the call is made)
Example: -RemoteHost “10.1.2.3” -OutputPath “\\WB-SYSTEM\D$\RADCOMM\output.txt”
(This additional parameter will help eliminate maintaining individual script file on SAP Server for each Radiation system)
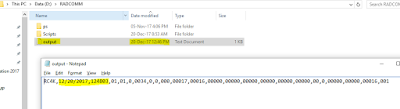
4. Create a folder on WB PC at D:\RADCOMM
(data will be written in a file output.txt in this folder)
If the OS call of SM49 command is successfully called, then the radiation data will be written in the output.txt file. This file will be read from the WB PC (Locally from front end) and SAP Screens will be populated accordingly.
5. ABAP Code to call the command ZGET_RADIATION maintained in SM49
You have to basically call the Function Module SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE with two parameters namely, the IP Address of Radiation System and the output path where the output will be saved.
CONCATENATE '-RemoteHost "' wa_zsrsw-radip
'" -OutputPath "\\' wa_zsrsw-term '\D$\RADCOMM\output.txt"'
INTO v_param.
CALL FUNCTION 'SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE'
EXPORTING
commandname = 'ZGET_RADIATION' "v_oscmd
additional_parameters = v_param
operatingsystem = sy-opsys
IMPORTING
status = v_status
exitcode = v_exitcode
TABLES
exec_protocol = i_cmdresult
EXCEPTIONS
no_permission = 1
command_not_found = 2
parameters_too_long = 3
security_risk = 4
wrong_check_call_interface = 5
program_start_error = 6
program_termination_error = 7
x_error = 8
parameter_expected = 9
too_many_parameters = 10
illegal_command = 11
wrong_asynchronous_parameters = 12
cant_enq_tbtco_entry = 13
jobcount_generation_error = 14
OTHERS = 15.
IF sy-subrc <> 0.
v_ossysubrc = sy-subrc.
CASE sy-subrc.
WHEN 1. v_errtxt = 'ATG:You do not have permission to get Radiation Data'.
WHEN 2. CONCATENATE 'ATG:Command' v_oscmd 'Not Found' INTO v_errtxt SEPARATED BY ''.
WHEN OTHERS. CONCATENATE 'ATG:Error in calling command' v_oscmd INTO v_errtxt SEPARATED BY ''.
ENDCASE.
MESSAGE v_errtxt TYPE 'I' DISPLAY LIKE 'E'.
ENDIF.
Trouble Shooting:
You might face some common issues which I am listing below:
1. Authorization
Please note that end users should have the following authorization to get the radiation values:
Authorization Object: S_LOG_COM
2. Folder Permission
Folder on WB PC D:\RADCOMM should be shared with Read/Write permission
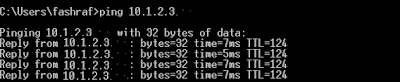
3. Pinging the IP.
Ping the IP of the radiation system to check if this is ON or not.
4. Run SM49 Directly
Still if you don’t get the data then run SM49 Command manually with following parameters:
-RemoteHost “<Radiation IP>” -OutputPath “\\<Your PC Name>\D$\RADCOMM\output.txt”
(First create a folder RADCOMM on your PC at D Drive and share it with all)
The command might take some time during first run. If there is any error, then it will be displayed as shown below.
Note that the IP 10.1.2.3 is not reachable.
However, if the IP is correct and then there will be no messages in the message part
And you can check the result in RADCOMM folder –> output.txt







No comments:
Post a Comment