Let me ask you, what do you think about the flow diagram below?
Left most image is often called “spaghetti wiring mess” , second one is an “organized and labelled wiring” and last two are the SAP icons for ‘Code’ and ‘Coffee’ respectively. Obviously I am at the last stage in this flow ! So let me explain a little bit about ‘Code’ while having this ‘Coffee’.
Developing software is fun for coding enthusiasts. It is indeed a lot of fun for experimentation, however when customers pay you for the software you create and maintain, it is a lot of responsibility on the designers and developers to deploy solution without causing maintenance nightmares. This is when the design patterns becomes very handy !
Design Patterns
Design patterns are primarily techniques envisaged by much experienced developers in order to solve common design problems in most efficient way by improving re-usability, maintainability, readability and extensibility of the software. There are many design patterns most developers are familiar with to name a few are – MVC , Factory, Singleton, Observer , Decorator etc. Today I will talk about Chain of Responsibility (CoR) pattern with a use case. Before we start, let me briefly touch upon the widely acclaimed principles in the OO design known as – S.O.L.I.D principles introduced by Robert C Martin (Uncle Bob) .
SOLID Principles
Each letter in ‘SOLID’ represent one principle as explained below –
◉ Single Responsibility Principle
◉ A class can undergo changes only due to changes in one part of the specifications; meaning classes shall have unique reason to change
◉ Open-Closed Principle
◉ A class shall be open for extension but closed for modification
◉ Liskov substitution principle
◉ An object shall be replaceable with instances of its own sub types
◉ Interface segregation principle
◉ Many smaller interfaces segregated by their tasks are preferable than one complex interface ; Rely more on composition rather than inheritance
◉ Dependency inversion principle
◉ A piece of code shall not get re-compiled due to changes in lower level components; Rely more on abstractions rather than concrete implementation.
With these principles in mind, let’s look at the pattern and the code
CoR Pattern Basics
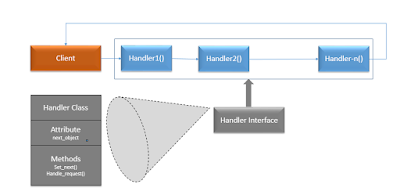
In CoR pattern a request from caller is propagated through a chain of handlers in which the relevant handlers perform a task in response and calls next handlers until chain is ended.
All request handler classes are derived from a common interface each implementations shall have the handler methods with unique business logic to perform an action.
The reference to next handler instance in the chain is stored in a private variable within each object
CoR pattern is most applicable in the following cases –
◉ A sequence of actions need to be executed upon an event
◉ Number of handlers and the order need to be determined at run time
◉ Handlers business logic is not related to each other
◉ Loose coupling between caller and handlers is desired
Use Case
Let’s say there is a requirement to trigger communication via various channels (email, sms, fax etc.) to business partners . Which channels are needed to be determined at runtime. Adding a new communication channel need to be plug-and-play with optimal testing required and no re-testing for other existing channels. It should be flexible to switch on/off a particular channel communication globally. Adding a new template of message (say new email message format) need to be quick and to be carried out with minimum testing required.
There are different ways to trigger messages, customize message templates etc. in ECC and S/4 by standard. But lets look at it from a custom abap development perspective this time.
How to fit this requirement to CoR pattern?
The crux of the design is an interface say request handler interface as explained above and all the handlers need to implement this interface. We can use factory pattern to instantiate each handler and all the handler classes need to be chained by adding reference to subsequent handlers in the private attribute.
Code Snippets
CoR Request handler interface
INTERFACE zif_cor_request_handler
PUBLIC .
* Reference to next handler in chain
DATA o_next_obj TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler .
* Factory method for instantiating chain handler
CLASS-METHODS get_chain_instance
IMPORTING
VALUE(is_variant) TYPE char10 OPTIONAL
EXPORTING
VALUE(er_object) TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler .
* Method to execute handler logic
METHODS handle_request
IMPORTING
!i_header TYPE zscor_header
!i_items TYPE ztcor_items
!i_control TYPE zscor_control .
METHODS set_next
IMPORTING
!er_next_object TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler .
ENDINTERFACE.
CoR Email handler factory
CLASS zcl_cor_email_handler DEFINITION
PUBLIC
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES zif_cor_request_handler .
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ALIASES o_next_obj
FOR zif_cor_request_handler~o_next_obj .
ENDCLASS.
CLASS ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER IMPLEMENTATION.
* <SIGNATURE>-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | Static Public Method ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER=>ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~GET_CHAIN_INSTANCE
* +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | [--->] IS_VARIANT TYPE CHAR10(optional)
* | [<---] ER_OBJECT TYPE REF TO ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER
* +------------------------------------------------------------------------</SIGNATURE>
METHOD zif_cor_request_handler~get_chain_instance.
CASE is_variant.
WHEN 'BILL'.
er_object = NEW zcl_cor_email_handler_billing( ).
WHEN 'DUNN'.
er_object = NEW zcl_cor_email_handler_dunning( ).
WHEN 'INFO'.
er_object = NEW zcl_cor_email_handler_info( ).
WHEN OTHERS.
er_object = NEW zcl_cor_email_handler( ).
ENDCASE.
ENDMETHOD.
* <SIGNATURE>------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | Instance Public Method ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER->ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~HANDLE_REQUEST
* +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | [--->] I_HEADER TYPE ZSCOR_HEADER
* | [--->] I_ITEMS TYPE ZTCOR_ITEMS
* | [--->] I_CONTROL TYPE ZSCOR_CONTROL
* +----------------------------------------------------------------------------</SIGNATURE>
METHOD zif_cor_request_handler~handle_request.
WRITE:/'-> Executing email handler'.
* <Implement handler logic here>
IF o_next_obj IS BOUND.
WRITE:/'........Calling next handler in chain.....'.
CALL METHOD me->o_next_obj->handle_request
EXPORTING
i_header = i_header
i_items = i_items
i_control = i_control.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.
* <SIGNATURE>--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | Instance Public Method ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER->ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~SET_NEXT
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | [--->] ER_NEXT_OBJECT TYPE REF TO ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------</SIGNATURE>
METHOD zif_cor_request_handler~set_next.
me->o_next_obj = er_next_object.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
CoR Email handler (Billing)
Subclass ‘zcl_cor_email_handler’ and re-define the ‘handle_request’ method
class ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER_BILLING definition
public
inheriting from ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER
create public .
public section.
methods ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~HANDLE_REQUEST
redefinition .
protected section.
private section.
aliases O_NEXT_OBJ
for ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~O_NEXT_OBJ .
ENDCLASS.
CLASS ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER_BILLING IMPLEMENTATION.
* <SIGNATURE>----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | Instance Public Method ZCL_COR_EMAIL_HANDLER_BILLING->ZIF_COR_REQUEST_HANDLER~HANDLE_REQUEST
* +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* | [--->] I_HEADER TYPE ZSCOR_HEADER
* | [--->] I_ITEMS TYPE ZTCOR_ITEMS
* | [--->] I_CONTROL TYPE ZSCOR_CONTROL
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------</SIGNATURE>
METHOD zif_cor_request_handler~handle_request.
WRITE:/'-> Executing email handler (Billing)'.
* <Implement handler logic here>
IF me->o_next_obj IS BOUND.
WRITE:/'........Calling next handler in chain.....'.
CALL METHOD o_next_obj->handle_request
EXPORTING
i_header = i_header
i_items = i_items
i_control = i_control.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
Similarly implement all other classes for sms, fax etc.
CoR Chain master control table
Create a table with appropriate data elements and maintain entries as shown below
Triggering program
Create a test triggering program as shown below
REPORT ztrigger_cor_request.
* CoR Chain related control table
DATA lt_controls TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF ztcor_controller.
DATA wa_control TYPE ztcor_controller.
* Holds CoR Objects to build chain
DATA o_corobj TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler.
DATA o_cormain TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler.
DATA o_nextobj TYPE REF TO zif_cor_request_handler.
DATA lv_variant TYPE char10 VALUE 'BILL'.
* Header, item and control parameters for handlers to implement logic
DATA wa_header TYPE zscor_header.
DATA lt_items TYPE ztcor_items.
DATA wa_contr TYPE zscor_control.
SELECT * FROM ztcor_controller INTO TABLE lt_controls WHERE active = 'X'.
LOOP AT lt_controls INTO wa_control.
IF o_corobj IS NOT BOUND.
CALL METHOD (wa_control-handler_class)=>zif_cor_request_handler~get_chain_instance
EXPORTING
is_variant = lv_variant
IMPORTING
er_object = o_corobj.
o_cormain = o_corobj.
ELSE.
CALL METHOD (wa_control-handler_class)=>zif_cor_request_handler~get_chain_instance
EXPORTING
is_variant = lv_variant
IMPORTING
er_object = o_nextobj.
CALL METHOD o_corobj->set_next EXPORTING er_next_object = o_nextobj.
o_corobj = o_nextobj.
ENDIF.
ENDLOOP.
WRITE:/ 'Entering handler chain..'.
CALL METHOD o_cormain->handle_request
EXPORTING i_header = wa_header i_items = lt_items i_control = wa_contr .
WRITE:/ '.. Handler chain Finished'.
Output
Trigger COR request - Testing
Entering handler chain..
-> Executing email handler (Billing)
........Calling next handler in chain.....
-> Executing fax handler
........Calling next handler in chain.....
-> Executing sms handler
.. Handler chain Finished
Extending the application
◉ Let’s assume in future , we need to add a new communication channel say – social media . We can achieve this by
◉ Create a new social media handler class referring to the request handler interface and implement the corresponding business logic in ‘handle_request’ method
◉ Add the channel configuration to the control table
Testing requirement – New class and its functionality only as none of other code re-compiles
◉ Let’s say we need to add a new email message template for ‘Escalation messages’. We can achieve this by –
◉ Subclass the email handler class and re-define the ‘handle_request’ method alone.
◉ Add the logic to create new handler class when criteria met.
Testing requirement – Required only for newly created class and its logic and it’s factory
Pros and Cons of CoR Pattern
Pros
◉ Flexible to add, remove and extend the handlers in the chain
◉ A runtime determination of handlers and sequencing is possible
Cons
◉ The caller have to wait until all the handlers in the chain has finished execution
◉ Every handler need to implement all the interface methods at least in main handler class



No comments:
Post a Comment