Introduction
Material creation in SAP is simpler using Fiori and Excel, we can tweak data before uploading, even integrating info from CAD software like SolidWorks or any other data source. This connection makes creating new materials in SAP a smoother process. Let’s dive into how this system works seamlessly.
Summary
In this blog, we’re diving into a streamlined material creation process within SAP. We’ll explore the creation of a Fiori app and an OData service designed to seamlessly integrate data from external sources for material creation. For this blog, we will be using data comes from SolidWorks automation.
Pre-requisites:
◉ S/4 HANA System
◉ VSCode with SAP Fiori Tools – Extension Pack
Step 1 – Preparing Excel sheet from any data source
We’ll kick off our material creation process by preparing an Excel sheet. Here, we’ll utilize data obtained from SolidWorks using a basic automation method. It’s crucial to note that this automation setup serves as an example, keeping things straightforward. In real-world scenarios, the process would involve selecting multiple assembly files or engaging in more intricate procedures for efficiency. This basic demonstration helps us understand the fundamental integration of SolidWorks data with our material creation system in SAP. The emphasis here is on demonstrating the foundational steps, which can be further expanded upon in practical implementations for more complex workflows.
This is the automation that helped to obtain data from Solidworks:
It’s important to note that the showcased automation is just a basic starting point and calls for improvement. While I used this simple automation, keep in mind that data retrieval from SolidWorks isn’t limited to automation alone. This automation is just for streamlining the process. You have the flexibility to gather information from SolidWorks manually or SolidWorks PDM, as well as from a wide array of any other data sources.
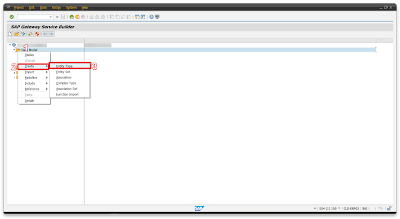
Step 2 – Creating oData service for material creation
We’ll create an oData service—a key connection allowing outside data, to smoothly enter SAP. This service acts as a bridge, ensuring easy communication between SAP and different external sources, vital for material creation within SAP.
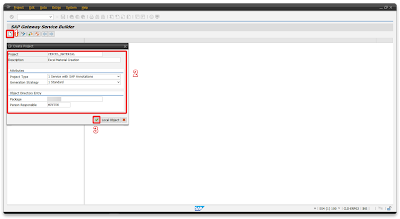
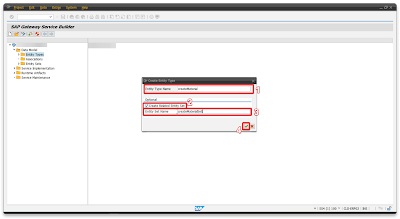
Step 2.1 – Creating oData service
Open your S/4 system and transaction SEGW
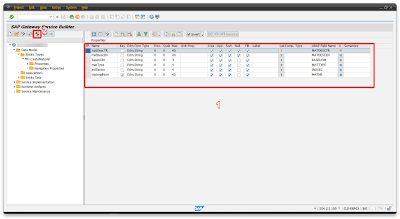
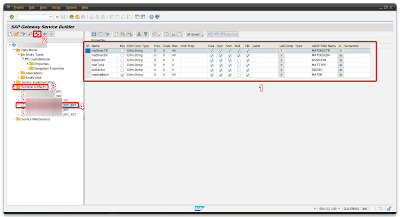
| Name | Key | Edm Core Type | Prec | Scale | Max | Abap Field Name |
| matDescTR | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 40 | MATDESCTR | |
| matDescEN | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 40 | MATDESCEN | |
| baseUOM | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 3 | BASEUOM | |
| matType | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 4 | MATTYPE | |
| indSector | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 4 | INDSEC | |
| materialNum | X | Edm.String | 0 | 0 | 40 | MATNR |
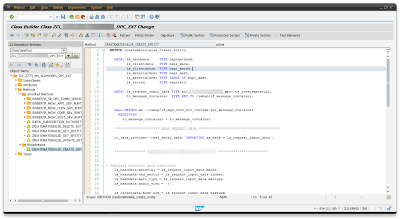
DATA: ls_headdata TYPE bapimathead,
ls_clientdata TYPE bapi_mara,
ls_clientdatax TYPE bapi_marax,
ls_materialdesc TYPE bapi_makt,
lt_materialdesc TYPE TABLE OF bapi_makt,
ls_return TYPE bapiret2.
DATA: ls_request_input_data TYPE zcl_zxxx_mpc=>ts_creatematerial,
lo_message_container TYPE REF TO /iwbep/if_message_container.
CALL METHOD me->/iwbep/if_mgw_conv_srv_runtime~get_message_container
RECEIVING
ro_message_container = lo_message_container.
"""""""""""""""""""""" READ REQUEST DATA """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
io_data_provider->read_entry_data( IMPORTING es_data = ls_request_input_data ).
""""""""""""""" INSERT DATA TO TABLE WITH BAPI """""""""""""""""""""""""
* Populate material data structure
ls_headdata-material = ls_request_input_data-matnr.
ls_headdata-ind_sector = ls_request_input_data-indsec.
ls_headdata-matl_type = ls_request_input_data-mattype.
ls_headdata-basic_view = 'X'.
ls_clientdata-base_uom = ls_request_input_data-baseuom.
ls_clientdatax-base_uom = 'X'.
IF ls_request_input_data-matdescen IS NOT INITIAL.
ls_materialdesc-langu = 'EN'.
ls_materialdesc-matl_desc = ls_request_input_data-matdescen.
APPEND ls_materialdesc TO lt_materialdesc.
ENDIF.
IF ls_request_input_data-matdesctr IS NOT INITIAL.
ls_materialdesc-langu = 'TR'.
ls_materialdesc-matl_desc = ls_request_input_data-matdesctr.
APPEND ls_materialdesc TO lt_materialdesc.
ENDIF.
* Call BAPI to create material
CALL FUNCTION 'BAPI_MATERIAL_SAVEDATA'
EXPORTING
headdata = ls_headdata
clientdata = ls_clientdata
clientdatax = ls_clientdatax
IMPORTING
return = ls_return
TABLES
materialdescription = lt_materialdesc.
* Check for errors and return message
IF ls_return IS NOT INITIAL.
CALL METHOD lo_message_container->add_message_from_bapi
EXPORTING
is_bapi_message = ls_return
iv_add_to_response_header = abap_true " Flag for adding or not the message to the response header
iv_message_target = CONV string( ls_return-field ).
EXIT.
ELSE.
CALL METHOD lo_message_container->add_message
EXPORTING
iv_msg_type = /iwbep/cl_cos_logger=>error
iv_msg_id = 'ZTEST'
iv_msg_number = '000'
iv_msg_text = `An error occured.`
iv_add_to_response_header = abap_true. "add the message to the header
EXIT.
ENDIF.
er_entity = ls_request_input_data. "Fill Exporting parameter ER_ENTITY
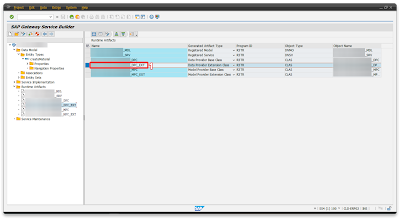
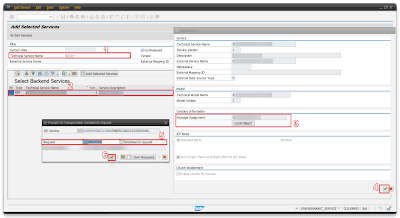
Step 2.2 – Registering oData service
Register the service in the backend on Tcode – /n/IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE
You registered service if you want you can test your service by clicking ‘2 – SAP Gateway Client’.
Step 3 – Creating Fiori app for excel upload and material creation
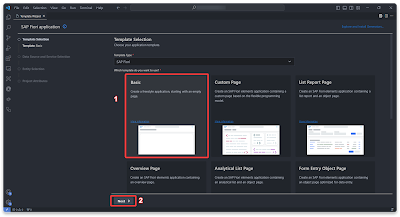
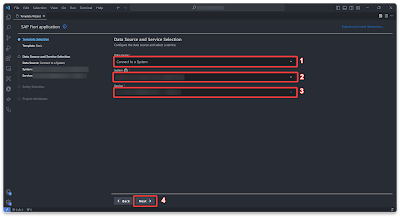
Step 3.1 – Creating Fiori app
We’ll construct a Fiori app using VSCode alongside the Fiori extension.
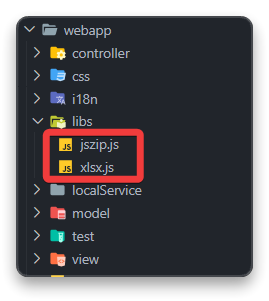
Step 3.2 – Adding libraries that will be used for excel import
We need to download the necessary JavaScript libraries for Excel import. Get the files from the links below:
◉ xlsx.js
◉ jszip.js
Once downloaded, create a folder named “libs” in the “webapp” directory and place these files inside it. These libraries are crucial for handling Excel imports in your Fiori app.
Step 3.3 – Creating global model in manifest.json
We’ll establish a JSON model in the manifest.json file to hold the data obtained from Excel and other sources. This model acts as a storage space within your Fiori app.
//...
"models": {
"i18n": {
"type": "sap.ui.model.resource.ResourceModel",
"settings": {
"bundleName": "<-- your namespace -->.i18n.i18n"
}
},
"globalModel": {
"type": "sap.ui.model.json.JSONModel",
"settings": {},
"preload": true
},
"": {
"dataSource": "mainService",
"preload": true,
"settings": {
"useBatch": false
}
}
},
//...
Step 3.4 – Preparing View
We’ll set up the user interface (UI) for our app using the provided code below. Code includes binding the previously created model to this view. This binding process ensures that the data stored in the model is displayed and accessible within the user interface.
<mvc:View
controllerName="<-- your namespace -->.controller.Main"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc"
displayBlock="true"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:u="sap.ui.unified"
xmlns:t="sap.ui.table"
xmlns:l="sap.ui.layout"
>
<Page
id="page"
title="{i18n>title}"
class="sapUiContentPadding sapUiContentPadding--header sapUiResponsivePadding--header sapUiResponsivePadding--subHeader sapUiResponsivePadding--content sapUiResponsivePadding--footer"
showNavButton="false"
showHeader="true"
>
<!-- ========================== -->
<!-- Excel Bar FlexBox -->
<!-- ========================== -->
<FlexBox
id="_IDGenFlexBox1"
wrap="Wrap"
class="sapUiMediumMarginTop"
justifyContent="Center"
>
<Input
id="searchInput"
width="100%"
editable="false"
value="{globalModel>/excelFileName}"
>
<layoutData>
<FlexItemData
id="_IDGenFlexItemData1"
growFactor="6"
/>
</layoutData>
</Input>
<FlexBox id="_IDGenFlexBox2">
<u:FileUploader
id="FileUploaderId"
class="sapUiSmallMarginBegin"
buttonText="Excel Upload"
sameFilenameAllowed="true"
iconOnly="false"
buttonOnly="true"
fileType="XLSX,xlsx"
icon="sap-icon://excel-attachment"
multiple="false"
iconFirst="true"
style="Emphasized"
change="handleImportData"
/>
</FlexBox>
</FlexBox>
<!-- ============= -->
<!-- Table -->
<!-- ============= -->
<t:Table
id="table"
rows="{
path:'globalModel>/materialsExcel',
sorter: {
path: 'SIMILARITY',
descending: true
}
}"
selectionMode="MultiToggle"
ariaLabelledBy="title"
visibleRowCount="20"
class="sapUiMediumMarginTop"
>
<t:extension>
<OverflowToolbar
id="_IDGenOverflowToolbar1"
style="Clear"
>
<Title
id="title"
text="Materials"
/>
<ToolbarSpacer id="_IDGenToolbarSpacer1" />
<Button
id="uploadButton"
type="Emphasized"
enabled="false"
icon="sap-icon://upload"
press="onPressUpload"
text="Upload"
class="sapUiSmallMarginBegin"
ariaDescribedBy="acceptButtonDescription genericButtonDescription"
/>
</OverflowToolbar>
</t:extension>
<t:rowSettingsTemplate>
<t:RowSettings
id="rowSettings"
highlight="{globalModel>status}"
highlightText="{globalModel>statusText}"
/>
</t:rowSettingsTemplate>
<t:columns>
<t:Column
width="8rem"
id="_IDGenColumn1"
>
<Label
id="_IDGenLabel1"
text="Status"
/>
<t:template>
<Text
busy="{globalModel>isBusy}"
id="_IDGenText2"
text="{globalModel>statusText}"
wrapping="false"
/>
</t:template>
</t:Column>
</t:columns>
</t:Table>
</Page>
</mvc:View>
Step 3.5 – Preparing Controller
In this part, while preparing the controller, our aim is to import data from Excel dynamically creating columns based on the Excel data. Subsequently, we’ll use this data to generate materials within our system, ensuring a smooth transfer of information from Excel to our system for material creation.
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller",
"../libs/xlsx",
"../libs/jszip",
],
/**
* @param {typeof sap.ui.core.mvc.Controller} Controller
*/
function (Controller, xlsx, jszip) {
"use strict";
return Controller.extend("<-- your namespace -->.controller.Main", {
onInit: function () {
},
handleImportData: function (oEvent) {
this._import(oEvent.getParameter("files") && oEvent.getParameter("files")[0]);
},
_import: function (file) {
var that = this;
var excelData = {};
if (file && window.FileReader) {
that.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty("/excelFileName", file.name);
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function (e) {
var data = e.target.result;
var workbook = XLSX.read(data, {
type: 'binary'
});
for (var i in workbook.SheetNames) {
excelData = XLSX.utils.sheet_to_row_object_array(workbook.Sheets[workbook.SheetNames[i]]);
break;
}
for (let index = 0; index < excelData.length; index++) {
excelData[index].statusText = 'Ready to Upload';
excelData[index].status = 'Information';
excelData[index].isBusy = false;
}
that.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty("/materialsExcel", excelData);
that._prepareTableColumns()
};
reader.onerror = function (ex) {
console.log(ex);
};
reader.readAsBinaryString(file);
}
},
onPressUpload: function (oEvent) {
var oTable = this.getView().byId('table');
var aSelectedIndex = oTable.getSelectedIndices();
var aMaterials = this.getView().getModel('globalModel').getProperty("/materialsExcel");
var aUploadMaterial = [];
aSelectedIndex.map(element => {
var aSelectedMat = aMaterials[element];
var oCreateData = {
"materialNum": aSelectedMat['PartNo'],
"matDescEN": aSelectedMat['DESCRIPTION'],
"baseUOM": aSelectedMat['BaseUOM'],
"matType": aSelectedMat['MatType'],
"indSector": aSelectedMat['IndustrialSector']
}
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/isBusy`, true);
this.getOwnerComponent().getModel().create("/createMaterialSet", oCreateData, {
success: $.proxy(function (data, resp) {
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/isBusy`, false);
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/status`, 'Success');
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/statusText`, 'Material Created');
},
this),
error: $.proxy(function (oError) {
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/isBusy`, false);
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/status`, 'Error');
this.getView().getModel('globalModel').setProperty(`/materialsExcel/${element}/statusText`, 'An error Occured');
}, this)
});
});
},
_prepareTableColumns: function () {
var oTable = this.getView().byId('table');
var oTableExtPoint = new sap.ui.table.extensions.Pointer(oTable);
var aTableCatalog = Object.keys(this.getView().getModel('globalModel').getProperty("/materialsExcel")[0])
aTableCatalog.map(aElement => {
if (aElement !== 'statusText' && aElement !== 'status' && aElement !== 'isBusy') {
var oLabel = new sap.m.Title({
text: aElement
});
var oTemplate = new sap.m.Text({ text: `{globalModel>${aElement}}`, wrapping: false })
var oColumn = new sap.ui.table.Column({
label: oLabel,
width: "10rem",
template: oTemplate,
filterProperty: aElement,
defaultFilterOperator: "Contains"
})
oTable.addColumn(oColumn);
}
})
var aTableColumns = oTable.getColumns();
for (var i = aTableColumns.length; i >= 0; i--) {
oTableExtPoint.doAutoResizeColumn(i);
}
this.getView().byId('FileUploaderId').setEnabled(false);
this.getView().byId('uploadButton').setEnabled(true);
},
});
});
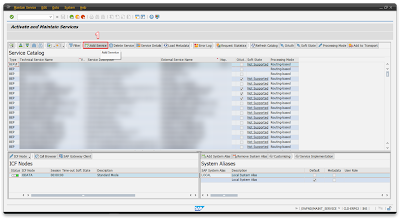
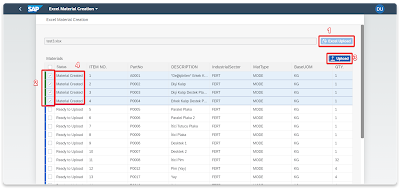
Step 4 – Use app and check system to ensure creating of materials
In last step, it’s time to utilize the app to create data within your system. Before doing so, it’s crucial to emphasize the need to review and tailor the entire system according to your specific requirements. Once revised, proceed to use the app to generate data within your system. This step enables you to validate and ensure the smooth creation of materials as intended in your system.




No comments:
Post a Comment