In this blog we will try to give a layman’s viewpoint regarding 3 W’s (What, Why and Where) of credit management. What is the basic definition and business justification for having credit management and how the SAP credit management has evolved/changed from ECC to S/4 i.e. depicting the key changes/differences between two set ups and in the end following same with the baseline configurations required in S/4 to make it work.
Credit management is defined as a risk mitigation process in which company sells a product(s) to a customer but collect money from the customer after a certain time. SAP Credit Management is an application that helps organizations monitor, evaluate, and control credit situations and credit allocations. It allows us to grant credit terms to our customers and also perform credit checks on the sales transactions.
When we implement Credit Management in our SAP instance we map our organization’s credit policies into the Credit Management application. Customers are aligned with these credit policy rules on the basis of the information collected from various sources, such as the customer’s past transnational history, the customer’s credit reports available from credit agencies like Dun & Bradstreet (D&B), the customer’s financial stability in the market, the geographical and political situations of the regions where the goods are sold, and so on.
Each credit-related sales transaction is then monitored and evaluated with respect to these rules or policies and the results of the evaluation help our organization decide whether to sell the goods on credit.
Credit check is a comparison of the customer’s credit exposure with the customer’s available credit limit setup in the credit master records. Credit exposure is a sum total of the open orders, open deliveries, open billings, open receivables, and open special liabilities. Credit limit is the maximum amount for which we allow our customer to purchase goods from us on credit. We store credit limits in the customer’s credit master records.
Whenever we create a new document that is relevant for credit checks, SAP calculates the current credit exposure for the customer and compares it with the customer’s available credit limit that is maintained in the customer’s credit master. If the exposure is more than the credit limit, the credit check fails an example of applying credit management in a sales cycle.
ECC Credit Management
In SAP ECC, credit management is part of sales and distribution module. Basically there are two types of credit management possible and below listed are basic features for controlling the functionality and behavior as per the business requirement
1. Simple credit check
◉ Here system compares customer credit limit with the total of all open item values and current sales order against a user pre-defined fixed credit limit for given customer. When the credit limit is exceeded, system sends a warning message for the customer.
◉ In simple credit check, the exposure of a customer at any point of time is sum total of all open item values and the sum of current sales order
◉ Open item values are defined as all those Sales Order(s) that has been saved, delivered, billed & transferred to FI but the payment is not received from the customer.
◉ Current sales order – Sales order that have been saved but not yet delivered.
1. Automatic credit check
◉ In automatic check some additional credit facilities are provided to a customer and here system behaves in a more subjective way for a customer than the simple check. In here even if a customer exceeds his set pre-define credit limit in SAP system, he can still place an order because of good purchase history. The following are two types of automatic credit check.
1. Static credit limit determination– Credit check by getting credit exposure after comparing total value of open sales, delivery, billing documents and open items
2. Dynamic credit limit determination– Credit Check by parameters mentioned above plus taking into consideration a time horizon which is business defined (week/month etc.)
In order to facilitate the credit management process we need to define & make the required assignments of sales area to customer credit control area and maintain the required credit management settings in the transactions OVA6/7/8. We need to then maintain credit master data settings (FD32) from where we can check and govern attributes like overall credit limit, credit exposure and limit used, payment status and history.
In S4H, credit management is part of Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM) and overall FSCM has different components mentioned below which can be utilized independently or in a combination to make best collaborative use of the financial supply chain:
◉ Credit Management (Used for Monitoring and control of credit risk from a central system)
◉ Dispute Management (Used for discrepancy processing between organization & customers)
◉ Collections Management (Used for Risk management and customer relations perspective)
◉ Biller Direct (Used for E-payments and integration of customer with financial services)
Key Features of S4/HANA FSCM Credit Management
◉ Widely distributed system landscapes can be monitored and controlled for customer credit risk from a central system
◉ In built scoring rules engine allows creation of customer scores using own rules. These scores can also be combined with external credit agencies as well like Equifax, Transunion
◉ The scores can be used to calculate and assign customer specific credit limits either automatically or manually
◉ Provision of Simplified interface for exchange of information with external credit agencies*
◉ Predefined reports are available for strategic credit analysis with credit controller specific dash boards
◉ Standard workflow is provided for credit limit request by sales Credit approval & reject options for controllers are available
◉ Inclusive credit cases and documented credit decisions for accounts. The documents can be created and approved. The cases can be used for legal or dispute actions
◉ All customers are created as Business Partner (BP) in FSCM credit management. Organizations can maintain details for scoring credit rules, credit limits, documenting collateral, exceptions and credit defaults
For the link to an external credit agency, an xml formatted file can be added as project work or the data can be input manually on the Business Partner as a part of the base license. An additional license is required to use the cloud-based link to credit agencies. The cloud-based service provides about 20-30 credit agencies such as Dun & Bradstreet right out of the box.
FUNCTIONAL CAPABILITIES: COMPARISON FEATURES OF S/4HANA FSCM CREDIT MANAGEMENT
What is Credit Management?
Credit management is defined as a risk mitigation process in which company sells a product(s) to a customer but collect money from the customer after a certain time. SAP Credit Management is an application that helps organizations monitor, evaluate, and control credit situations and credit allocations. It allows us to grant credit terms to our customers and also perform credit checks on the sales transactions.
Why is Credit Management Required?
When we implement Credit Management in our SAP instance we map our organization’s credit policies into the Credit Management application. Customers are aligned with these credit policy rules on the basis of the information collected from various sources, such as the customer’s past transnational history, the customer’s credit reports available from credit agencies like Dun & Bradstreet (D&B), the customer’s financial stability in the market, the geographical and political situations of the regions where the goods are sold, and so on.
Each credit-related sales transaction is then monitored and evaluated with respect to these rules or policies and the results of the evaluation help our organization decide whether to sell the goods on credit.
Where and How Credit Management Works?
Credit check is a comparison of the customer’s credit exposure with the customer’s available credit limit setup in the credit master records. Credit exposure is a sum total of the open orders, open deliveries, open billings, open receivables, and open special liabilities. Credit limit is the maximum amount for which we allow our customer to purchase goods from us on credit. We store credit limits in the customer’s credit master records.
Whenever we create a new document that is relevant for credit checks, SAP calculates the current credit exposure for the customer and compares it with the customer’s available credit limit that is maintained in the customer’s credit master. If the exposure is more than the credit limit, the credit check fails an example of applying credit management in a sales cycle.
High Level ECC Credit Management Vs S4H Credit Management
ECC Credit Management
In SAP ECC, credit management is part of sales and distribution module. Basically there are two types of credit management possible and below listed are basic features for controlling the functionality and behavior as per the business requirement
1. Simple credit check
◉ Here system compares customer credit limit with the total of all open item values and current sales order against a user pre-defined fixed credit limit for given customer. When the credit limit is exceeded, system sends a warning message for the customer.
◉ In simple credit check, the exposure of a customer at any point of time is sum total of all open item values and the sum of current sales order
◉ Open item values are defined as all those Sales Order(s) that has been saved, delivered, billed & transferred to FI but the payment is not received from the customer.
◉ Current sales order – Sales order that have been saved but not yet delivered.
1. Automatic credit check
◉ In automatic check some additional credit facilities are provided to a customer and here system behaves in a more subjective way for a customer than the simple check. In here even if a customer exceeds his set pre-define credit limit in SAP system, he can still place an order because of good purchase history. The following are two types of automatic credit check.
1. Static credit limit determination– Credit check by getting credit exposure after comparing total value of open sales, delivery, billing documents and open items
2. Dynamic credit limit determination– Credit Check by parameters mentioned above plus taking into consideration a time horizon which is business defined (week/month etc.)
In order to facilitate the credit management process we need to define & make the required assignments of sales area to customer credit control area and maintain the required credit management settings in the transactions OVA6/7/8. We need to then maintain credit master data settings (FD32) from where we can check and govern attributes like overall credit limit, credit exposure and limit used, payment status and history.
S4H Credit Management
In S4H, credit management is part of Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM) and overall FSCM has different components mentioned below which can be utilized independently or in a combination to make best collaborative use of the financial supply chain:
◉ Credit Management (Used for Monitoring and control of credit risk from a central system)
◉ Dispute Management (Used for discrepancy processing between organization & customers)
◉ Collections Management (Used for Risk management and customer relations perspective)
◉ Biller Direct (Used for E-payments and integration of customer with financial services)
Key Features of S4/HANA FSCM Credit Management
◉ Widely distributed system landscapes can be monitored and controlled for customer credit risk from a central system
◉ In built scoring rules engine allows creation of customer scores using own rules. These scores can also be combined with external credit agencies as well like Equifax, Transunion
◉ The scores can be used to calculate and assign customer specific credit limits either automatically or manually
◉ Provision of Simplified interface for exchange of information with external credit agencies*
◉ Predefined reports are available for strategic credit analysis with credit controller specific dash boards
◉ Standard workflow is provided for credit limit request by sales Credit approval & reject options for controllers are available
◉ Inclusive credit cases and documented credit decisions for accounts. The documents can be created and approved. The cases can be used for legal or dispute actions
◉ All customers are created as Business Partner (BP) in FSCM credit management. Organizations can maintain details for scoring credit rules, credit limits, documenting collateral, exceptions and credit defaults
For the link to an external credit agency, an xml formatted file can be added as project work or the data can be input manually on the Business Partner as a part of the base license. An additional license is required to use the cloud-based link to credit agencies. The cloud-based service provides about 20-30 credit agencies such as Dun & Bradstreet right out of the box.
FUNCTIONAL CAPABILITIES: COMPARISON FEATURES OF S/4HANA FSCM CREDIT MANAGEMENT
| Functionality | ECC Credit Management | FSCM Credit Management |
| Master Data | Customer | Business Partner |
| Finance Data | FI-AR | FI-AR, FI-CA |
| Credit Exposure Monitoring | Only at the level of the credit control area Specific simple system landscape (1xSD, 1xFI) SAP system only |
At segment and main level (overall credit limit) Distributed system landscape (multiple FI, SD and CRM systems) SAP and non-SAP |
| Scoring & Rating for customer | Not Available | Credit Rules Engine |
| Credit Information-External Credit Agencies | Only through Partner Products | Any XML based credit information service |
| Credit Limit Rules | Not Available | Credit Rules Engine |
| Credit Case | Not Available | Credit Limit Requests |
| Documented Credit Decisions | Not Available | Documented Credit Decisions |
| Work Flow | Only in SD | Any credit event, documented credit decisions, credit limit requests |
| Analysis | Customer Fact Sheet | Fiori Apps, HANA Live, OLAP/OLTP including BW content |
| Relationships | Not Available | Hierarchy Relationships |
| Non SAP Connectivity | Not Available | XI Server |
SAP Cloud for Credit Integration
An additional option for credit integration is the SAP Cloud for Credit Integration application service. SAP S/4HANA Cloud for credit integration allows us to use external credit risk information in order to make better credit decisions and to automate the monitoring of our customers’ credit risk.
Features:
◉ Connect to the world’s leading credit bureaus
◉ Seamless integration of credit risk evaluation and reports delivered by credit agencies
◉ More than 10 agencies already available
Credit Management Configuration in S/4 HANA
Below are the configuration steps for Credit Management in S/4 HANA.
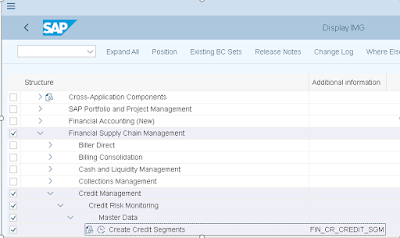
Step 1: Define Credit Segment
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Credit Risk Monitoring>Master Data> Create Credit Segments
Make new entries and save
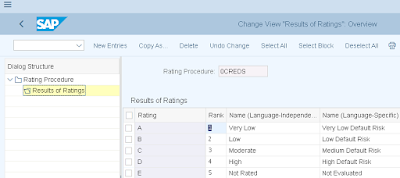
In case we are using external credit Information agencies then we need to create Rating Procedure whereby we need to ensure that the external information providers are connected to an interface {Credit Information Query out (Query Credit Information from External Data Providers) in the namespace http://sap.com/xi/FSCM} via the XI infrastructure
Settings for Rating Procedure are as under:
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Credit Risk Monitoring>Master Data> Define Rating Procedure
New Entries,
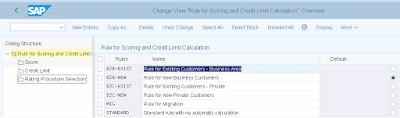
This rating procedure, we need to assign with credit limit calculation,
Select the created rule and click on score, credit limit and rating procedure.
ID Type = For ex. Credisafe
Step 2: Define Customer Credit Group
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Credit Risk Monitoring>Master Data> Define Customer Credit Group
In SAP S/4 HANA, the Credit Management Calculation has enhanced with formula editor function button. Following are the calculation formula criteria:
1. Currency
2. Credit Segment
3. Score
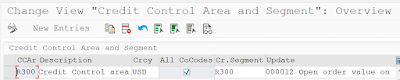
Step 3: Assign Credit Control Area and Credit Segment. Transaction Code: UKM_SEGMENT
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Assign Credit Control Area and Credit Segments
New Entries and Once assignment done with credit control area and credit segment, then save it.
Step 3: Assign Sales Area to Credit Control Area (same steps as in SAP ECC system)
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Assign Sales Area to Credit Control Area
Step 4: Enter Settings
Condition Partner: Update the subtotal with value “A” for Credit Release check for NET VALUE condition type
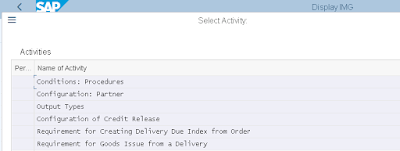
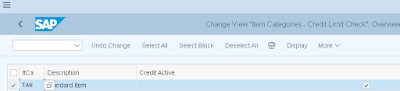
Step 5: Determine Active Receivable Per Item Category. Transaction Code: OVA7
Path: IMG>SD>Sales>Sales Document Item> Define Item Category
Activate as per required Item Category
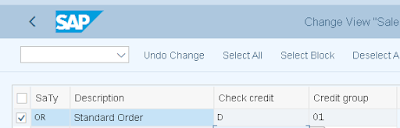
Step 6: Define Credit Group. Transaction Code: OVA6
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Define Credit Group
We can create our own credit group as per requirement
Step 7: Assign Sales Document and Delivery Document
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Assign Sales Documents and Delivery Documents
Credit Management can be updated at the Delivery Level as well if required.
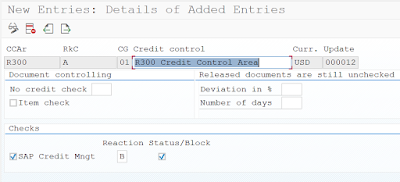
Step 8: Define Automatic Credit Control. Transaction Code: OVA8
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Define Automatic Credit Control
The check box “SAP credit management” activates a BADI (BADI_SD_CM) which has 2 methods one for sale order and the other for delivery:
Order: FSCM_CREDIT_CHECK_ORDER
Delivery: FSCM_CREDIT_CHECK_DELVRY
This BADI carries the data to the FSCM credit management during order creation/delivery, thus the checks defined in the FSCM credit management will become effective. So, the OVA8 transaction is now going to act as a trigger point to carry out SAP credit management (FIN-FSCM-CR)
Compared to the old credit management in ECC in S4H it has less settings due to the fact the checks are now controlled thru different transaction in FSCM. SAP credit management transaction OVA8 will still act as a control mechanism to activate/deactivate SAP credit management FIN-FSCM-CR but all further checks on the static, dynamic, max doc value etc. are all going to be carried out at in different transaction at FSCM.
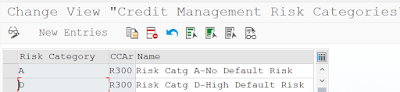
Step 9: Define Risk Category and Assignment
Path: IMG>FSCM>Credit Management>Integration with AR & SD>Integration with SD> Define Risk Categories
We need to activate the BADI for the following Credit Management in S/4 HANA.
Select the BADI and click on ACTIVATE button.
This complete the configuration procedure for the SAP S/4 HANA for FSCM Credit Management.
Customer Master Setup: Standard BP role for Credit Management is UKM000 – SAP CREDIT MANAGEMENT
Here we need to enter the Rules, Risk Class, Check Rule and Customer Group under Credit Profile tab, which will be under UKM000 BP role. After that we need to go to Credit Data Segment and fill up the value as shown in below snap shot
Update the value for Limit Defined, i.e. Credit Limit and save it.
This completes the Master Data Setup for FSCM Credit Management in SAP S/4 HANA.
O2C Process and FSCM Effects: After Credit Limit is exceeded, as the Risk Category kept as Error system will not allow to save the sales order.
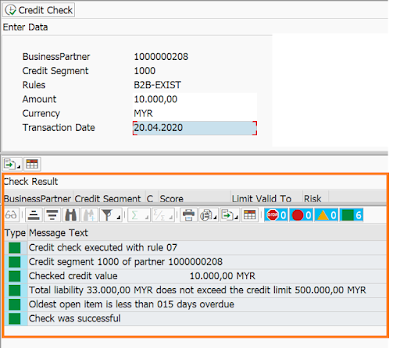
Handy Quick Tip to simulate Credit Management from BP to find errors / issues without having to go to Sales Orders ( The snippets used here are from a client sandbox system that is why the BP number and currency reflected is different than above snippets in the blog)
BP- > Credit Management -> Credit Segment Data -> Simulate Button As below through icon in red
Enter your details like Amount, Currency, Document Date for example from Sales Order and Press Credit Check Button on Screen, The Check Result is displayed as below
In line with the topic there is another blog posted by a colleague which has information regarding the S/4 credit management reports, tables and issues which were faced in our implementation.


















No comments:
Post a Comment