Prerequisites on Linux
A 64-bit Linux version is required because the ODBC driver for ABAP is a 64-bit ODBC driver. To define ODBC data source names (DSN) for the ODBC driver for ABAP on Linux, you need to install the unixODBC software package on your Linux system. This software package will also provide some simple command-line tools to test an ODBC connection and to execute SQL queries.
You may also want to install the LibreOffice software package to follow my simple application scenario.
Download and unpack ODBC driver on Linux
To install the “ODBC driver for ABAP”, you need to visit the SAP Support Portal and click on “Software Downloads”. After this you may need to log on and then you can search for components “ODBC DRIVER FOR ABAP 1.0” and “SAPCRYPTOLIB”. Make sure that you download the correct SAR files for the Linux operating system. In addition you may need to download “SAPCAR” to be able to unpack the SAP files (SAPCAR -xvf <SAR file>).
Choose a directory as your ODBC driver location (for example, /home/<myuser>/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP ) and unpack the SAR files in this directory. The directory will now contain at least the following files:
libsapcrypto.so
sapgenpse
ODBC_driver_for_ABAP.h
ODBC_driver_for_ABAP.so
libicudata65.so
libicudecnumber.so
libicui18n65.so
libicuuc65.so
Create an ODBC data source and test the ODBC connection
The unixODBC ODBC driver manager package provides several configuration files that can be used for defining an ODBC driver and DSNs. You can list the file locations by executing the command “odbcinst -j”.
> odbcinst -j
unixODBC 2.3.6
DRIVERS............: /etc/unixODBC/odbcinst.ini
SYSTEM DATA SOURCES: /etc/unixODBC/odbc. [MYDSN]>
FILE DATA SOURCES..: /etc/unixODBC/ODBCDataSources
USER DATA SOURCES..: /home/myuser/.odbc.ini
SQLULEN Size.......: 8
SQLLEN Size........: 8
SQLSETPOSIROW Size.: 8
Here we will use only the file /home/myuser/.odbc.ini to define both the driver and a user-specific DSN. Creating a system-wide driver definition and DSN can be done in a similar way.
The .odbc.ini file needs to contain the DSN-specific connection parameters for the ODBC driver for ABAP as described in SAP Note 3076454.
Create the file /home/<myuser>/.odbc.ini and insert the following content:
[MYDSN]
; this is a comment
Driver=/home/<myuser>/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP.so
HOST=<hostname>
PORT=443
CLIENT=100
LANGUAGE=EN
SERVICEPATH=/sap/bc/sql/sql1/sap/S_PRIVILEGED
TrustAll=true
CryptoLibrary=/home/<myuser>/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP/libsapcrypto.so
UidType=alias
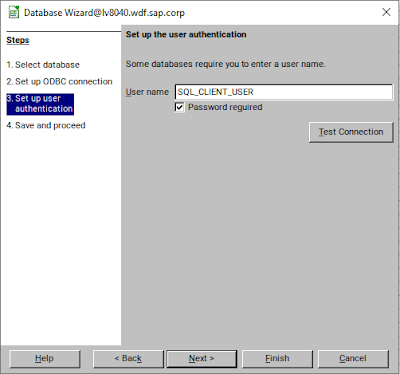
Here we just included the driver definition in the .odbc.ini file using the driver key word. As connect user for our test system, we will use the user SQL_CLIENT_USER that was created as an alias user in the SAP BTP ABAP environment. It is also possible to store the UID/PWD properties in the .odbc.ini file. However, we do not recommend this for security reasons. Again, for simplicity sake, we did not bother to create a PSE file and used the “TrustAll=True” property.
After defining the DSN, you can immediately use the unixODBC tools isql or iusql to test the ODBC connection. Both tools work but since the ODBC driver for ABAP is a Unicode-only driver, I usually prefer to use the iusql tool. If everything is configured correctly, you should see the following:
> iusql MYDSN SQL_CLIENT_USER <password> -v
+---------------------------------------+
| Connected! |
| |
| sql-statement |
| help [tablename] |
| quit |
| |
+---------------------------------------+
SQL>
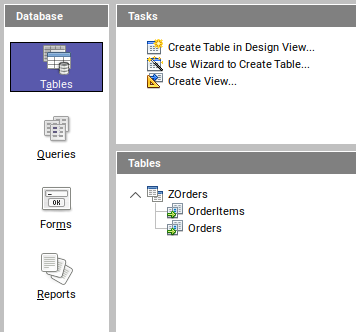
The ODBC connection has now been opened successfully and you can use the command “help” to display all exposed CDS entities and you can also execute first SQL queries.
SQL> help
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------+
| TABLE_CAT| TABLE_SCHEM| TABLE_NAME| TABLE_TYPE| REMARKS|
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------+
| | ZOrders | OrderItems| VIEW | ORDER ITEMS|
| | ZOrders | Orders | VIEW | ORDERS |
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------+
SQLRowCount returns 2
2 rows fetched
SQL> select * from ZOrders.Orders
+-----------+-------------+
| Id | CreationDate|
+-----------+-------------+
| 0000000001| 20210801 |
| 0000000002| 20210802 |
| 0000000003| 20210803 |
+-----------+-------------+
SQLRowCount returns 3
3 rows fetched
Note: The tool isql can also be used to open a DSN-less connection by providing all connection properties directly in the command line, using a semicolon separated SQLDriverManager connection string (for unknown reasons the Unicode tool iusql does not support the “-k” option).
> isql -v -k "Driver=/home/<myuser>/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP.so;HOST=<hostname>;PORT=443;CLIENT=100;LANGUAGE=EN;SERVICEPATH=/sap/bc/sql/sql1/sap/S_PRIVILEGED;TrustAll=true;CryptoLibrary=/home/<myuser>/ODBC_driver_for_ABAP/libsapcrypto.so;UidType=alias;UID=SQL_CLIENT_USER;PWD=<pwd>;"
+---------------------------------------+
| Connected! |
| |
| sql-statement |
| help [tablename] |
| quit |
| |
+---------------------------------------+
SQL>
LibreOffice as ODBC Client Application Example
For this blog post about the ODBC client with Linux, we will use LibreOffice as an ODBC client application.
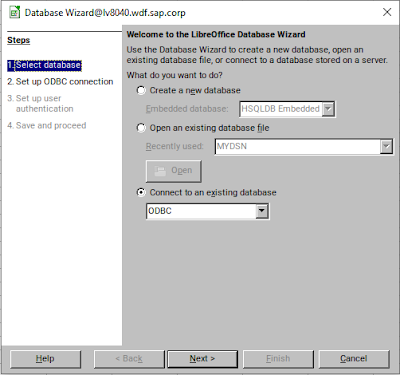
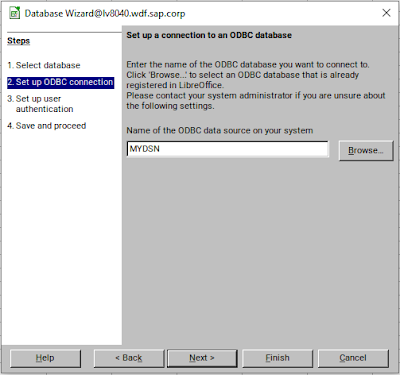
Start LibreOffice and choose either “Database” or “Calc Spreadsheet” as a starting point. In “Calc”, choose “File” -> “New” -> “Database” and select “ODBC” under the “Connect to an existing database” option.

No comments:
Post a Comment